Powerful Solutions for Harmonic Distortion
We are CTM Magnetics. We specialize in engineering harmonic filters and sine wave filters that remove harmonic distortion, giving you efficient and reliable power quality solutions.

Industries We Serve
We are the foundation beneath the roaring success of an array of sectors. Our unwavering commitment to innovation ensures that each sector receives tailored solutions to meet their unique needs and challenges, empowering them to thrive in their respective fields.
Innovative Solutions Empowered by CTM Patented Technology
When it comes to power systems, CTM Magnetics is “built to lead.” Our power quality solutions are engineered to outlast the toughest challenges and exceed industry standards.
-
EV Inverter Testing
-
Harmonic Filters
Air & Liquid CooledGridHawk® harmonic filters are engineered to eliminate harmonic distortion and enhance power quality.
-
Sine Wave Filters
Air & Liquid CooledCTM output Sine Wave Filters eliminate switching harmonics produced by VFDs, protecting motors.
-
Reactors
Air & Liquid CooledCTM input and output reactors mitigate harmonic distortion on the input and output of VFDs.
-
Transformers
Air & Liquid CooledCTM 3-phase transformers are the ideal choice when extreme shock & vibe capability or liquid cooling is required.
-
Custom Solutions
Fit your project NeedsCustomized power quality solutions tailored to your unique needs, helping you solve your specific power quality challenges.
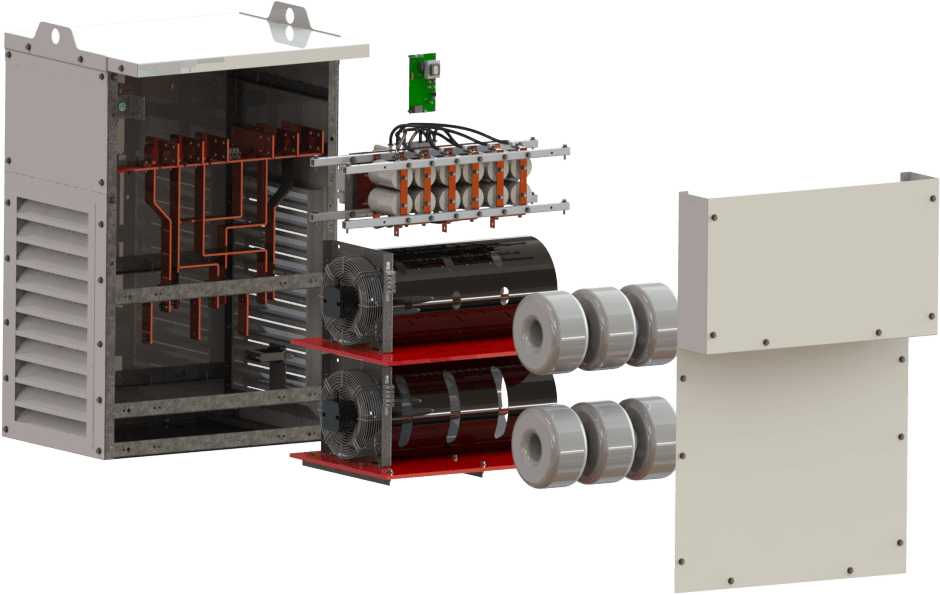
The CTM Advantage
Innovative Solutions Empowered by CTM Patented Technology
We stand out with engineering excellence, industry-leading technology, and tailored solutions that exceed expectations. Backed by decades of experience, rapid response times, and unmatched expertise, we solve your power quality problems with exceptional service and reliability.
Partnering with top-tier companies spanning various industries, we have established a reputation for working with the best, delivering exceptional solutions that drive success.

